




# 흐름 제어 ( 조건문, 반복문)
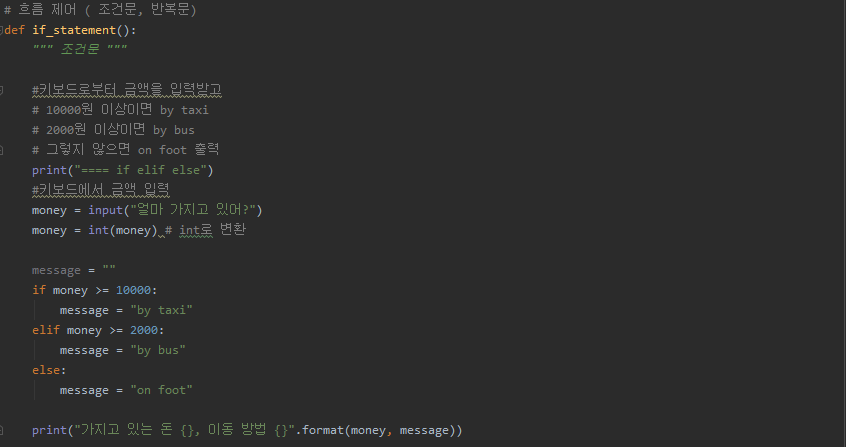
def if_statement():
""" 조건문 """
#키보드로부터 금액을 입력받고
# 10000원 이상이면 by taxi
# 2000원 이상이면 by bus
# 그렇지 않으면 on foot 출력
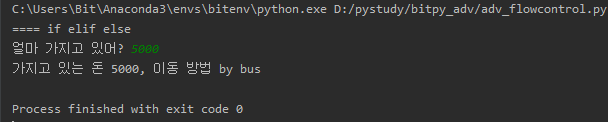
print("==== if elif else")
#키보드에서 금액 입력
money = input("얼마 가지고 있어?")
money = int(money) # int로 변환
message = ""
if money >= 10000:
message = "by taxi"
elif money >= 2000:
message = "by bus"
else:
message = "on foot"
print("가지고 있는 돈 {}, 이동 방법 {}".format(money, message))
def if_expr():
""" 조건 표현식"""
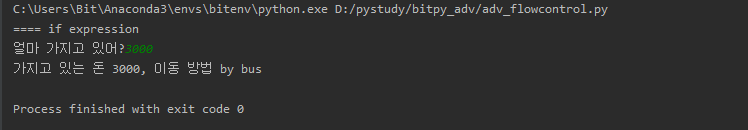
print("==== if expression")
money = int(input("얼마 가지고 있어?"))
message = "by taxi" if money >=10000 \
else "by bus" if money >= 2000 \
else "on foot"
print("가지고 있는 돈 {}, 이동 방법 {}".format(money, message))
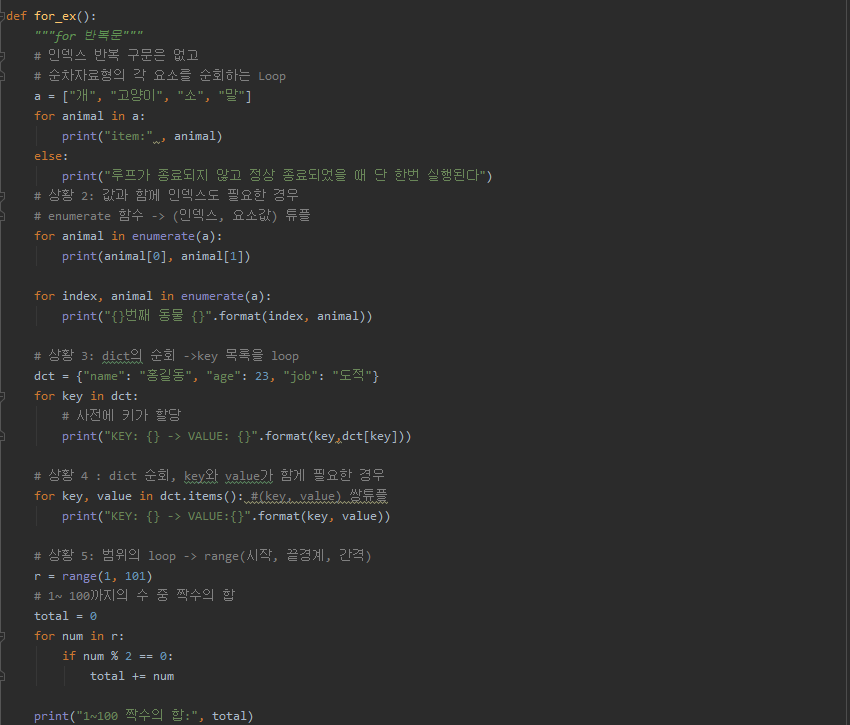
def for_ex():
"""for 반복문"""
# 인덱스 반복 구문은 없고
# 순차자료형의 각 요소를 순회하는 Loop
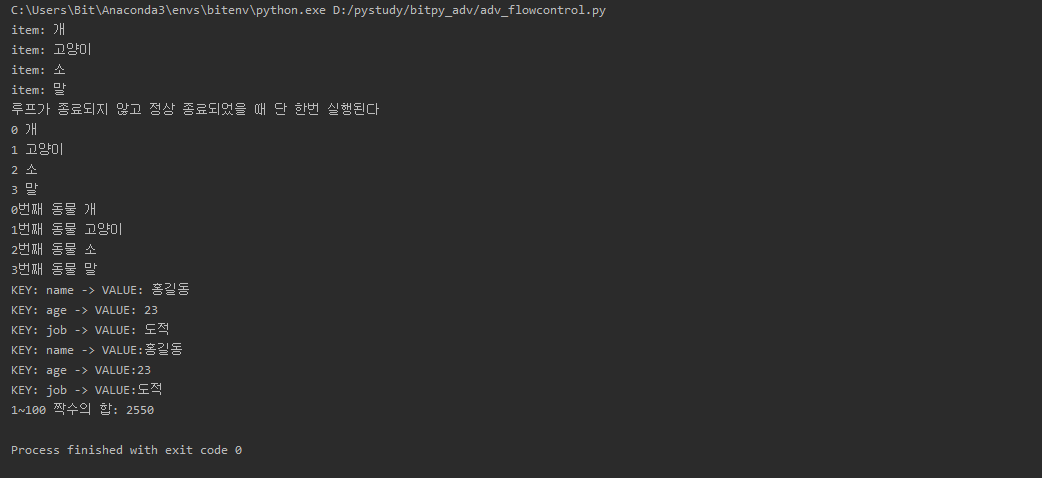
a = ["개", "고양이", "소", "말"]
for animal in a:
print("item:" , animal)
else:
print("루프가 종료되지 않고 정상 종료되었을 때 단 한번 실행된다")
# 상황 2: 값과 함께 인덱스도 필요한 경우
# enumerate 함수 -> (인덱스, 요소값) 튜플
for animal in enumerate(a):
print(animal[0], animal[1])
for index, animal in enumerate(a):
print("{}번째 동물 {}".format(index, animal))
# 상황 3: dict의 순회 ->key 목록을 loop
dct = {"name": "홍길동", "age": 23, "job": "도적"}
for key in dct:
# 사전에 키가 할당
print("KEY: {} -> VALUE: {}".format(key,dct[key]))
# 상황 4 : dict 순회, key와 value가 함게 필요한 경우
for key, value in dct.items(): #(key, value) 쌍튜플
print("KEY: {} -> VALUE:{}".format(key, value))
# 상황 5: 범위의 loop -> range(시작, 끝경계, 간격)
r = range(1, 101)
# 1~ 100까지의 수 중 짝수의 합
total = 0
for num in r:
if num % 2 == 0:
total += num
print("1~100 짝수의 합:", total)
# 연습 문제1. 구구단을 출력
# 연습문제 2. 삼각형을 그려주세요
"""
****
***
**
*
"""
#continue : 아래에 남아있는 문장은 더이상 실행하지 않고 다음번 loop로 이동
# break : 루프를 더이상 진행하지 않고 루프 밖으로 탈출
def while_ex():
# 특정 조건이 만족되는 동안 루프를 실행
# 조건을 True로 부여하면 무한 루프가 생성된다
# 1부터 100까지 숫자 중에서 짝수만 합산(While 버전)
i = 1
total =0
while i<= 100:
if i % 2 == 0:
total += i
i += 1
else:
print("루프가 정상 종료되면 실행")
print(total)
def list_comp():
"""List Comprehension"""
# 기존 순차자료형을 기반으로 조건에 맞는 데이터를 추출
# 연산식을 수행하여 새로운 리스트를 만들어 낸다
# Synyax: [표현식 for 항목 in 순회가능 객체 if 조건]
# 기존 방식
data = range(1,11)
# data 객체를 제곱해서 새 리스트를 만들자
results = []
for num in data:
results.append(num * num)
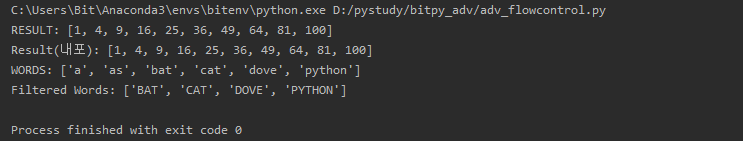
print("RESULT:", results)
results = []
#리스트 내포 방식
results = [num*num for num in data]
print("Result(내포):", results)
#내포시 if 표현식을 연결하면 조건에 맞는 데이터만 추출 할 수 있다
# 연산에 포함시킬 수 있다
words = "a as bat cat dove python".split() #list
print("WORDS:", words)
# words(str list)에서 요소의 길이가 3글자 이상인
# 요소들만 추출 새 리스트를 만들자
filtered = [word.upper() for word in words if len(word) >=3 ]
print("Filtered Words:", filtered)
#연습 문제
# 1~ 100까지의 수 중에서 짝수의 리스트를 새로 만들기
number = range(1,101)
filtered = [num*1 for num in number if num % 2 == 0]
print(filtered)
def set_comp():
""" Set Comprehension """
# Syntax : { 표현식 for 객체 in 순회가능 객체 }
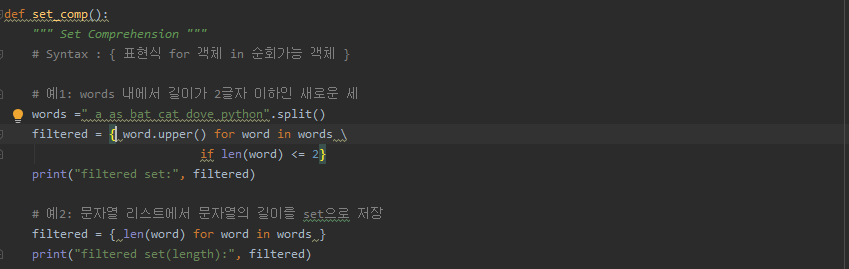
# 예1: words 내에서 길이가 2글자 이하인 새로운 세
words =" a as bat cat dove python".split()
filtered = { word.upper() for word in words \
if len(word) <= 2}
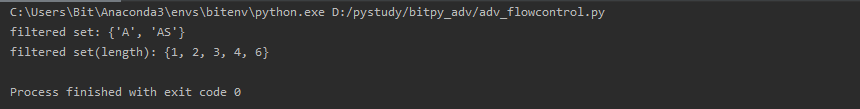
print("filtered set:", filtered)
# 예2: 문자열 리스트에서 문자열의 길이를 set으로 저장
filtered = { len(word) for word in words }
print("filtered set(length):", filtered)
def dict_comp(): #comp = comprehension(이해력)
""" 사전의 내포 """
# Syntax: {키표현식: 값표현식 for 객체 in 순회가능객체}
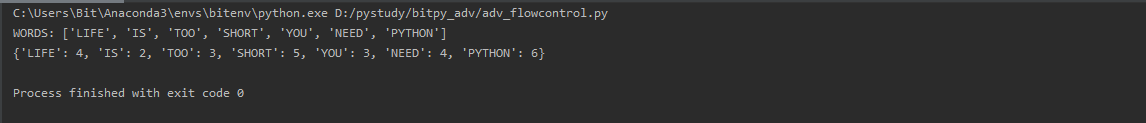
words = "Life is too short You need Python".upper().split()
print("WORDS:",words)
#키로는 개별 단어, 값으로는 해당 단어의 길이
dct = {word:len(word) for word in words}
print(dct)
if __name__ == "__main__":
#if_statement()
#if_expr()
#for_ex()
#while_ex()
#list_comp()
#set_comp()
dict_comp()
'2020 > Python' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Python handling Exception, raise Exception, 예외, 처리, except (0) | 2019.11.20 |
|---|---|
| 함수의 스코핑(Scope),가변인자, 고정인가, 키워드인자 (0) | 2019.11.20 |
| Python 객체(deepcopy, copy, global, local) (0) | 2019.11.20 |
| Python 기초문제(3문제) (0) | 2019.11.19 |
| Python 순차 자료형(Sequence) 내장 함수(range,enumerate,zip) (0) | 2019.11.19 |



