Client 클래스
package application;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.Socket;
//한명의 클라이언트와 통신하게 해주는 클래스 입니다.
public class Client {
//소켓이 있어야지 클라이언트와 네트워크상에서 통신할 수 있음.
Socket socket;
//생성자 생성
public Client(Socket socket) {
this.socket = socket;
//반복적으로 클라이언트로부터 메시지를 전달받을 수 있도록 receive()함수를 만듬.
receive();
}
//클라이언트로부터 메시지를 전달받는 메소드.
public void receive() {
//작업 생성은 Runnable 인터페이스 or Callable 인터페이스를 구현한 클래스로 작업요청할 코드를 삽입해 작업을 만들 수 있습니다.
//둘의 차이점은 Runnable의 run() 메서드는 리턴값이 없고, Callable의 call() 메서드는 리턴 값이 있습니다.
Runnable thread = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
//반복적으로 클라이언드에게 내용을 받을 수 있도록 while문 생성
while(true) {
//어떤 내용을 전달 받을 수 있도록 inputstream객체 사용
InputStream in = socket.getInputStream();
//버퍼를 사용해서 한번에 512byte까지 받을 수 있도록 설정
byte[] buffer = new byte[512];
//메시지의 크기
int length = in.read(buffer);
while(length == -1) throw new IOException();
//서버에 접속을 한 클라이언트의 주소정보 출력, 스레드의 이름값을 출력,
System.out.println("[메시지 수신 성공]"
+ socket.getRemoteSocketAddress()
+ ":" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
//전달받은 값을 한글도 포함 할 수 있도록 UTF-8 설정
String message = new String(buffer, 0, length, "UTF-8");
//전달받은 메시지를 다른 클라이언트들에게 보낼 수 있도록 만들어 줍니다.
for(Client client : Main.clients) {
client.send(message);
}
}
}catch(Exception e){
try {
System.out.println(" [메시지 수신 오류]"
+ socket.getRemoteSocketAddress()
+ " : " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}catch(Exception e2){
e2.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
};
//메인함수에 있는 스레드풀에 섭밋을 해줍니다.
//즉 스레드풀에 만들어진 하나의 스레드를 등록
Main.threadPool.submit(thread);
}
//클라이언트에게 메시지를 전송하는 메소드.
public void send(String message) {
Runnable thread = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
OutputStream out = socket.getOutputStream();
byte[] buffer = message.getBytes("UTF-8");
//버퍼에 담긴 내용을 서버에서 클라이언트에게 전송
out.write(buffer);
out.flush();
}catch(Exception e){
try {
System.out.println("[메시지 송수신 오류]"
+ socket.getRemoteSocketAddress()
+ " :" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
Main.clients.remove(Client.this);
socket.close();
}catch(Exception e2) {
e2.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
};
Main.threadPool.submit(thread);
}
}
Main class
package application;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Vector;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
public class Main extends Application {
//스레드 풀 사용(한정된 자원으로 안정적이게 서버를 운용하기 위해서 threadPool 기법을 사용합니다.)
public static ExecutorService threadPool;
//접속한 클라이언트들을 관리 할수 있도록 만듬.
public static Vector<Client> clients = new Vector<Client>();
//서버 소켓 생성
ServerSocket serverSocket;
//서버를 구동시켜 클라이언트의 연결을 기다리는 메소드.
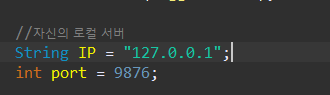
public void startServer(String IP, int port) {
try {
serverSocket = new ServerSocket();
//특정한 ip번호와 port번호로 특정한 클라이언트에게 접속을 기다리게 해줌
serverSocket.bind(new InetSocketAddress(IP, port));
}catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
//서버 소켓이 닫혀있는 경우가 아니라면
if(!serverSocket.isClosed()) {
stopServer();//서버를 종료
}
return;
}
// 클라이언트가 접속할 때 까지 계속 기다리는 스레드.
Runnable thread = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
//계속해서 새로운 클라이언트가 접속 할 수 있도록 해줌
while(true) {
try {
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();
clients.add(new Client(socket));
System.out.println(" [클라이언트 접속] "
+ socket.getRemoteSocketAddress()
+ " :" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}catch(Exception e) {
// 서버 소켓에 문제가 생긴거니 서버를 종료 시키고 break문을 활용해서 빠져나갑니다.
if(!serverSocket.isClosed()) {
stopServer();
}
break;
}
}
}
};
//스레드 풀을 초기화
threadPool = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
//클라이언트에 접속을 원하는 스레드를 넣어줍니다.
threadPool.submit(thread);
}
//서버의 작동을 중지시켜주는 메소드
public void stopServer() {
try {
//현재 작업중인 모든 소켓 닫기
Iterator<Client> iterator = clients.iterator();
//한명 한명의 클라이언트에게 접근
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
Client client = iterator.next();
client.socket.close();
iterator.remove();
}
//서버 소켓 객체 닫기
if(serverSocket != null && !serverSocket.isClosed()) {
serverSocket.close();
}
//스레드풀 종료
if(threadPool != null && !threadPool.isShutdown()) {
threadPool.shutdown();
}
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//UI를 생성하고 , 실질적으로 프로그램을 동작시키는 메서드
@Override
public void start(Stage primaryStage) {
}
//프로그램의 메인 메서드
public static void main(String[] args) {
launch(args);
}
}
다음 글에서 계속 하겠습니다.